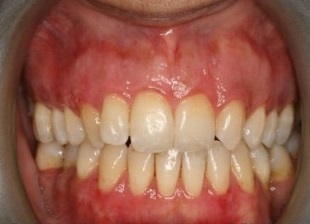
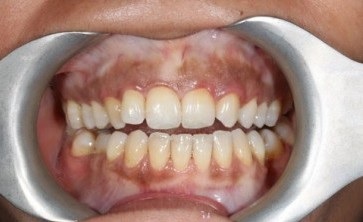
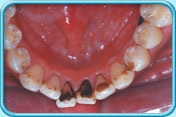
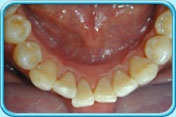
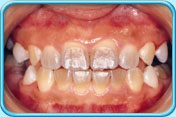
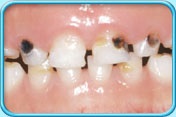
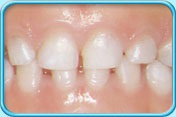
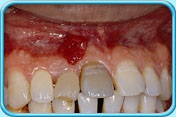
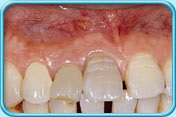
Scaling and root planing is a deep cleaning below the gumline used to treat gum disease.
Gum disease is caused by a sticky film of bacteria called plaque. Plaque is always forming on your teeth, but if they aren’t cleaned well, the bacteria in plaque can cause your gums to become inflamed. When this happens, your gums will pull away from your teeth and form spaces called pockets. Plaque then gets trapped in these pockets and cannot be removed with regular brushing. If untreated, gum disease could lead to bone and tooth loss.
If gum disease is caught early and hasn’t damaged the structures below the gum line, a professional cleaning should do. If the pockets between your gums and teeth are too deep, however, scaling and root planning may be needed.
This deep cleaning has two parts. Scaling is when your dentist removes all the plaque and tartar (hardened plaque) above and below the gumline, making sure to clean all the way down to the bottom of the pocket. Your dentist will then begin root planing, smoothing out your teeth roots to help your gums reattach to your teeth. Scaling and root planing may take more than one visit to complete and may require a local anesthetic.
After a deep cleaning, you may have pain for a day or two and teeth sensitivity for up to a week. Your gums also may be swollen, feel tender and bleed.
To prevent infection, control pain or help you heal, your dentist may prescribe a pill or mouth rinse. Your dentist may also insert medication (sub-antimicrobial-dose doxycycline) directly into the pocket that was cleaned.
Your dentist will schedule another visit to see how your gums have healed and measure the depth of your pockets. If they have gotten deeper, more treatment may be needed.
Good dental care at home is essential to help keep gum disease from becoming more serious or recurring. Brush your teeth twice a day with a soft brush, clean between your teeth daily, eat a balanced diet, avoid using tobacco and see your dentist regularly.
– What is Halitosis (Bad Breath)?
Halitosis, commonly known as bad breath, is an embarrassing health condition that affects approximately 30% of people around the world. Additional medical terms for this condition include stomatodysodia, fetor oris, and ozostomia. Regardless of the term used, this is the presence of a foul-smelling odor that seems to come from the mouth cavity. According to the Academy of General Dentistry, in more than 90% of cases, the odor originates in the mouth, throat, and tonsils. Although this is something everyone experiences at one time or another, if your case does not improve after brushing, flossing, and rinsing the mouth with an alcohol free mouthwash, it may be chronic.
The foul oral odour is usually caused by a group of anaerobic, sulfur-producing bacteria that breed beneath the surface of the tongue and often in the throat and tonsil area. The term “anaerobic” literally means living without oxygen, and in fact, these bacteria do not require oxygen to live. They occur naturally in the oral environment and are essential because they assist in digestion by breaking down proteins into amino acids. Proteins are commonly found in food, mucus or phlegm, blood, and in diseased oral tissue.
As these bacteria feast on proteins in your mouth, sulphur compounds are released from the back of your tongue and throat. The bacteria excrete waste as hydrogen sulfide, methyl mercaptan, and other odorous and bad tasting compounds known as volatile sulphur compounds. As long as the anaerobic bacteria feed on proteins and excrete volatile sulfur compounds unchecked, your breath will become worse and worse.
Four Common Bad Breath Causes
There are many underlying causes of halitosis, but four of them are very common.
Dry mouth: Xerostomia, the medical term for dry mouth, provides a perfect environment for anaerobic bacteria reproduction. Long periods of speaking, smoking, drinking alcohol, and snoring are a few common underlying causes. Most people experience foul breath in the morning due to lack of saliva production while they sleep. For healthy individuals, food odors are temporary and normal salivary flow will eliminate them within several minutes. However, those who suffer from dry mouth and lack of saliva find that even minor food odors may lead to long-term issues.
Foods: Halitosis can be exacerbated by certain foods such as onions and garlic because they contain smelly sulfur compounds, while dairy, meat, and fish contain dense proteins which are used as a food source by the anaerobic, sulfur-producing bacteria. Refined and processed sugars also provide a food source for bacteria. Coffee and juices can contribute to this problem because they are acidic and provide these bacteria with an ideal breeding environment.
Poor dental hygiene: Inadequate oral care causes bacterial buildup on the teeth and gums. Teeth cannot shed their surfaces the way skin can, so microorganisms can easily attach to the teeth and remain there for extended periods. If they are not continuously removed by adequate brushing, these bacteria develop into something called biofilm, commonly known as dental plaque. When plaque is allowed to accumulate near the gumline, it will harden and begin destroying teeth and gum tissues due to intense bacterial activity. This leads to gum disease such as gingivitis and periodontitis, which enable proteins from bleeding gums and diseased oral tissue to fuel odor-causing bacteria. Tooth decay and poorly fitting or dirty dentures can also contribute to this problem.
Illness and disease: According to studies, an estimated 10% of all halitosis cases are caused by certain illnesses. Individuals who suffer from diabetes, lung disease, kidney disease, cancer, liver disease, respiratory tract infections, or metabolic disorders often experience chronic foul breath due to dry mouth. Sinusitis, pneumonia, bronchitis, postnasaldrip, and polyps affect the airways and may also contribute to the problem. Other common illnesses associated with bad breath include nasal odor and tonsil stones, yeast infections of the mouth, and gum disease. Certain drugs such as antidepressants, high blood pressure medications, and antihistamines can factor into dry mouth because they reduce saliva production.
Illness and disease: According to studies, an estimated 10% of all halitosis cases are caused by certain illnesses. Individuals who suffer from diabetes, lung disease, kidney disease, cancer, liver disease, respiratory tract infections, or metabolic disorders often experience chronic foul breath due to dry mouth. Sinusitis, pneumonia, bronchitis, postnasaldrip, and polyps affect the airways and may also contribute to the problem. Other common illnesses associated with bad breath include nasal odor and tonsil stones, yeast infections of the mouth, and gum disease. Certain drugs such as antidepressants, high blood pressure medications, and antihistamines can factor into dry mouth because they reduce saliva production.
Note: Halitosis is rarely associated with life-threatening diseases. However, it is important that you consult your doctor or dentist as soon as you notice consistent white spots on the tonsils and sores in the mouth with or without a fever. Sometimes bad breath is triggered by severe health conditions such as throat or mouth cancers, human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection, digestive system disorders, or diabetes – and further, can indicate dehydration or zinc deficiency. Taking proper care of your teeth and visiting the dentist at least twice a year are the easiest ways to avoid these issues.
Offensive breath tells us that something is out of balance. In fact, anthropologists have reported that once humans started to kiss each other, the ability to smell one another’s breath became a very important way to test a partner’s compatibility. If the other person didn’t pass the smell test, they were not able to get to the next step towards securing a mate.
Halitosis is a medical condition that lowers self-esteem and affects everyday life and personal relationships. People with chronic or recurring bad breath often lose their self-confidence. It can be difficult to know if you have this problem, because it is often challenging to pick up on one’s own scent. Furthermore, family members and colleagues may not feel comfortable telling you. One of the best ways to find out if you have foul breath is to lick the inside of your wrist, wait five seconds, and then take a whiff.
Most symptoms of halitosis depend on the underlying cause. The most common symptoms include postnasal drip, a bitter metallic taste, a white coating on the tongue, and thick saliva. Many individuals who have foul breath associated with dry mouth can experience difficulty speaking or swallowing, a burning sensation in the mouth, or dry eyes. Fever, sore throat, persistent cough, and swollen lymph nodes in the neck indicate respiratory tract infections, which can also be a contributing factor.
Getting a Proper Diagnosis
The best way to truly identify the source of chronic halitosis is to visit a dentist or doctor for a professional diagnosis. When you are ready to tackle this situation, be sure to be open and honest with the healthcare professional performing the examination. It is important for him or her to understand all the health problems you are experiencing in order to determine the underlying cause and recommend appropriate treatment.
The Halimeter (also known as a portable sulfide gas monitor) is the most commonly used clinical diagnostic instrument utilized in this field. It measures the concentration of hydrogen sulfide in parts per billion (ppb) in mouth air. The Halimeter uses a patented electrochemical voltammetric sensor, which has provided reproducible results to clinicians for the past 20 years. It has been demonstrated hundreds of times on national and local television by Dr. Harold Katz on programs such as “The View,Good Morning America”, and “CBS Morning News”.
For more than a century, pharmaceutical companies attempted to alleviate halitosis by using mouthwash that contained alcohol. This is the exact opposite of what should be done because alcohol is a drying agent. Clinicians have learned a good deal in the ensuing years, and in most cases, this condition can be successfully treated. Like the symptoms, treatment depends on the underlying cause.
It is important to keep in mind that you cannot eliminate the bacteria from the tongue that cause bad breath. Consequently, scraping or brushing the tongue is a temporary remedy at best, and is typically frustrating for those who believe tongue scraping or tongue brushing is a permanent solution. The bacteria that cause this are part of your normal oral flora and are essential to breaking down proteins, a key step in normal digestion.
A much simpler and clinically-proven method to treat bad breath is to interrupt the bacteria’s chemical production of odors by introducing oxygenating compounds to your oral environment. Oxygen is the natural enemy of the bacteria that cause this problem because they are anaerobes and cannot function in the presence of oxygen.
In general, a dentist will recommend mouthwashes and toothpastes that contain oxygenating agents such as chlorine dioxide or sodium chlorite to neutralize volatile sulfur compounds and help control odor causing bacteria found in the mouth.
If you are experiencing mouth dryness, your dentist will recommend a saliva substitute to moisten the mouth throughout the day. Some effective, natural ingredients to look for in oral care products are zinc gluconate, aloe vera, green tea, tea tree oil, xylitol, CoQ10, glycyrrhizic acid and oral probiotics like K12 and M18.
Six Bad Breath Home Remedies
The practice of a few, simple, self-care techniques can help to minimize halitosis. There are several things you can do at home.
12 Easy Ways to Prevent Bad Breath
Please remember, preventing halitosis is always easier than treating it. By developing the right habits, you can effectively help prevent it.
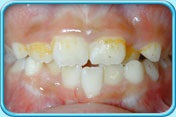
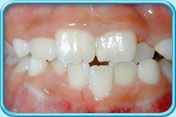
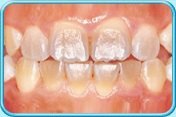
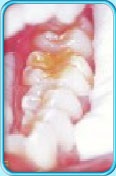
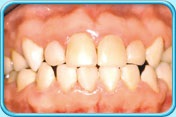
Factors causing tooth discoloration
There are two factors causing tooth discoloration — internal factor and external factor.
1. External factors causing tooth discoloration
2. Internal factors causing tooth discoloration
Dr. Vivek believes these systems provide complete and even cosmetic tooth whitening, while producing little or no sensitivity during and after treatment.