-
Call Today
+91-9414042882
-
Opening Hours
Mon–Sat: 09:00 AM–08:00 PM,
Sun: 10:00 AM–01:00 PM (By Appointment)
+91-9414042882
Mon–Sat: 09:00 AM–08:00 PM,
Sun: 10:00 AM–01:00 PM (By Appointment)
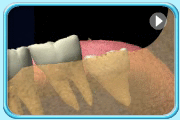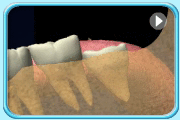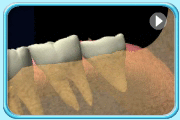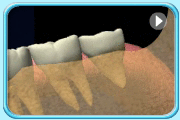
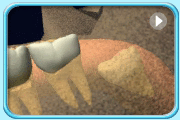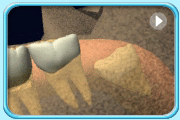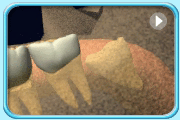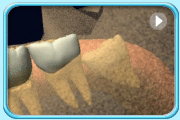
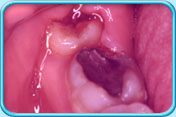
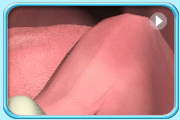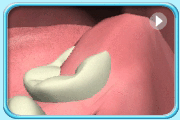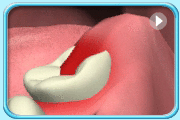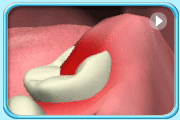
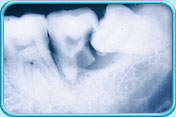

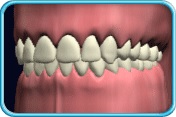
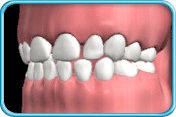
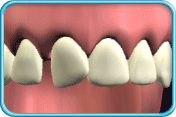
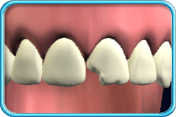
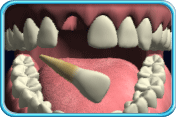
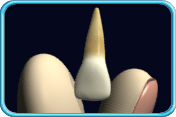


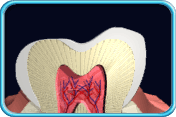
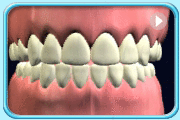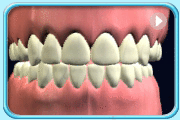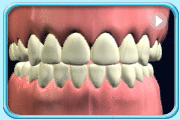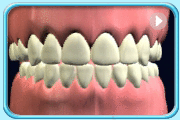
– Use of a toothbrush with bristles that are too hard, or brushing with excessive force
– Frequent consumption of highly acidic food or beverages
– Habitual grinding of teeth (bruxism)
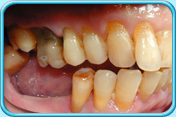
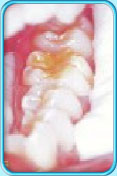
Top dental clinic in jaipur, Rajasthan, India.
Mon–Fri: 09:00 AM–08:00 PM
Sun: 10:00 AM–01:00 PM
(By Appointment Only)